Acronyms and Abbreviations
- AutoSar: Automotive Open System Architecture
- SWC: Software Component
- BSW: Basic Software
- SOME/IP(SOMEIP): Scalable service-Oriented MiddlewarE over IP
- IPC: Inter Process Communication
Overview
SOME/IP:
- SOMEIP middleware has been proposed to solve the problem of service unification and remote invocation within a network. This middleware is loacated at the application layer.
- Each SWC can use the SOMEIP interface to interact whit other SWCs through someipd(SOMEIP-Deamon).
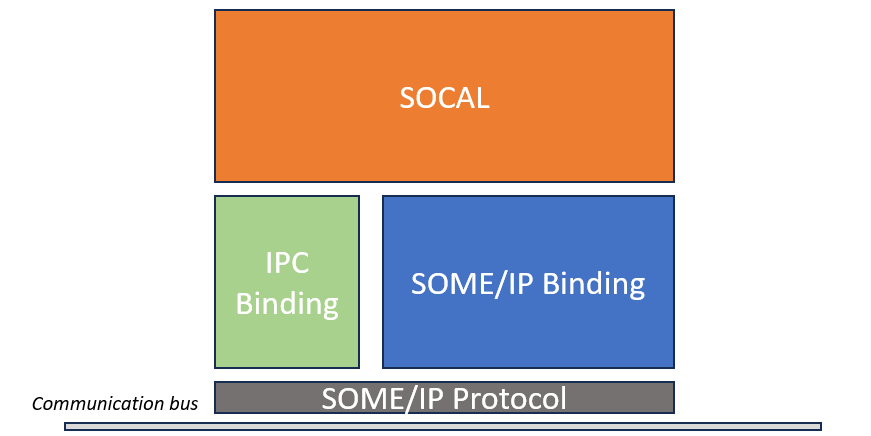
IPC:
- IPC refers to communication or information exchange between different processes. The methods include Pipline, FIFO, Semaphore, Socket, Streams and so on.
- In Autosar, IPC uses the protocol of SOME/IP and the CM implements the communication stack in BSW.
SOCAL:
- CM implements SOCAL, and the communication protocol is unified using SOME/IP protocol. So that either SWCs on the same ECU or SWCs on different ECUs can communicate via SOCAL without having to care the underlying communication method.
SOME/IP protocol
Applications can use SOME/IP to offer or acquire certain types of services. SOME/IP defines several service interface types:
Method
Methods are used for request/response communication patterns. They can be categorized into:
- Methods with return values: Client sends a request and expects a response
- Synchronous calls: Client waits for response
- Asynchronous calls: Client continues execution and handles response later
- Methods without return values (Fire & Forget): Client sends request without expecting response
Event
Events implement the publish/subscribe pattern:
- A consumer can subscribe to event messages from a provider
- The provider sends messages either:
- Periodically at configured intervals
- When event data changes
- Events are unidirectional (provider to subscriber)
- Multiple subscribers can receive the same event
Fields
Fields represent data elements that can be accessed remotely. They combine getter/setter methods with notifications:
-
Getter: Read access to field value
- Client requests current value
- Server responds with value
-
Setter: Write access to field value
- Client sends new value
- Server updates field
- Optional response confirms update
-
Notification: Change notification for field value
- Similar to events
- Subscribers receive updates when field value changes
- Can be configured for periodic updates
Message Structure
SOME/IP messages consist of:
|
|
- Message Header: Contains routing information
- Request ID: Identifies service and method
- Protocol Version: SOME/IP protocol version
- Interface Version: Service interface version
- Message Type: Request/Response/Notification/Error
- Return Code: Success/Error indication
- Payload: Actual data being transmitted
Service Discovery
SOME/IP includes a Service Discovery (SD) protocol that:
- Announces available services
- Handles service instance finding
- Manages subscribe/unsubscribe for events
- Supports service availability monitoring
Communication Patterns
SOME/IP supports multiple communication patterns:
- Client/Server (Request/Response)
- Publish/Subscribe (Events)
- Fire & Forget (One-way messages)
These patterns can be used over various transport protocols:
- TCP for reliable communication
- UDP for efficient broadcast/multicast
- IPC for local communication
